Servo position and speed mode control device speed comparison - Database & Sql Blog Articles
Now, the same mechanical conditions are used to compare the position and speed control modes and the stability of the servo motor running speed.
The Aluminum Alloy Creative Notebook Stand is stable and durable, stable and does not shake. Laptop Stand Ergonomic bone is supported by an aluminum alloy triangle-shaped stable structure, which has a strong load-bearing capacity and can easily carry 100 g items, and Laptop Stand Holder is stable and not easy to damage.
Aluminum Alloy Laptop Bracket,Laptop Stand To Keep Cool,Dell Laptop Vertical Stand,Aluminium Alloy Notebook Stand Shenzhen ChengRong Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.dglaptopstandsupplier.com
The mechanical transmission mode is the synchronous belt mode;
The servo motor is a R88M-G servo motor;
The driver is a R88D-GT type driver;
The host computer controller is CP1H-XA type plc.
First, the position control mode
1. Control wiring method during position control 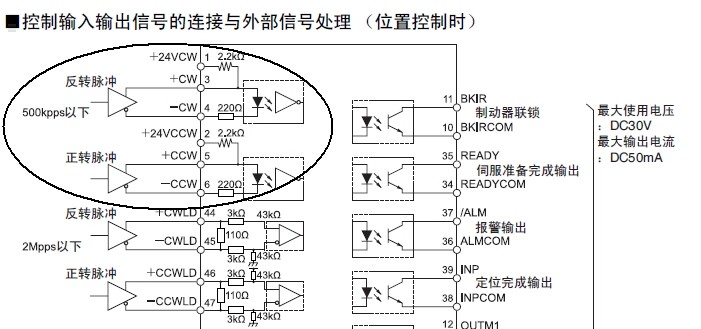
2. Required parameter setting: Pn02 (control mode selection) is set to 0.
In the position control, the operating frequency of the servo motor is mainly set by the SPED command in the host computer PLC.
3. When the position is controlled, use the CX-Drive software to monitor the speed curve of the servo motor. As shown below: 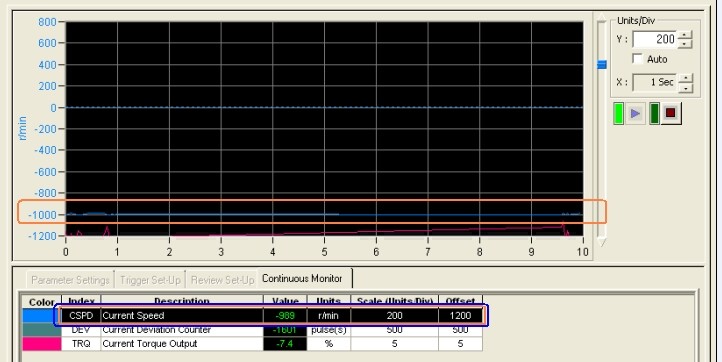
Second, the speed control mode
1. Control wiring method during speed control 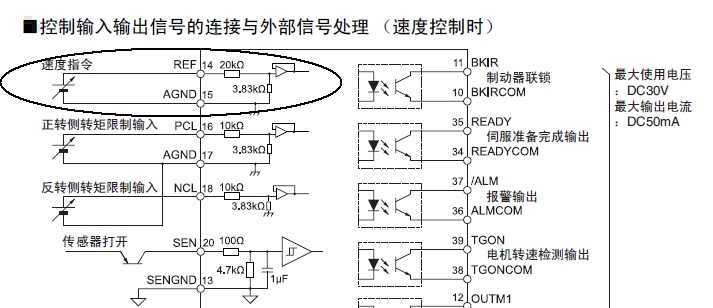
2. Required parameter setting: Pn02 (control mode selection) is set to 1.
The external 0-10V DC signal is input to the A/D of the PLC by the potentiometer, and then the servo motor operation is controlled by the D/A output of the PLC.
3. When speed control, use CX-Drive software to monitor the speed curve of the servo motor. As shown below: 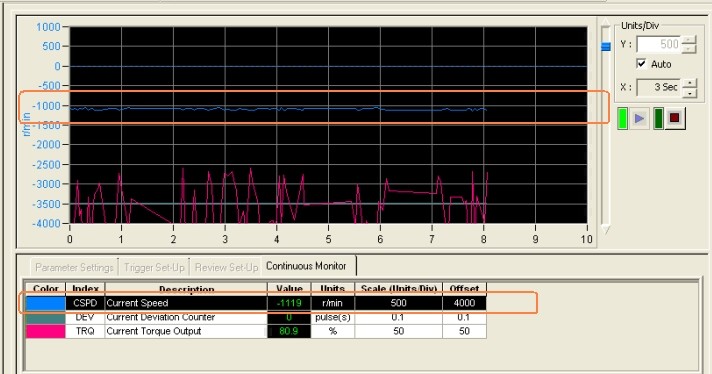
3. Summary According to the comparison in the above speed graph, the speed control in the position control mode is more stable than the speed control in the speed mode. After a long period of production operation, the speed of position mode control has been stable and meets the requirements of users. 