The United States launched a trade war against the "Made in China 2025", a war triggered by the fourth industrial revolution
The United States launched a trade war and aimed at "Made in China 2025". 5G will accelerate the fourth industrial revolution and has risen to a national strategic position. What is the relationship between them? A long article, read the reasons behind it. Dual Band Router Module,Dual Band Wifi Module,Dual Band Router Embedded Wifi Module,Gigabit Ethernet Router Module Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommtech.com
A war triggered by the fourth industrial revolution Humans have experienced three industrial revolutions. Every industrial revolution has brought about tremendous changes in the way humans have produced, and has also triggered wars of different forms. 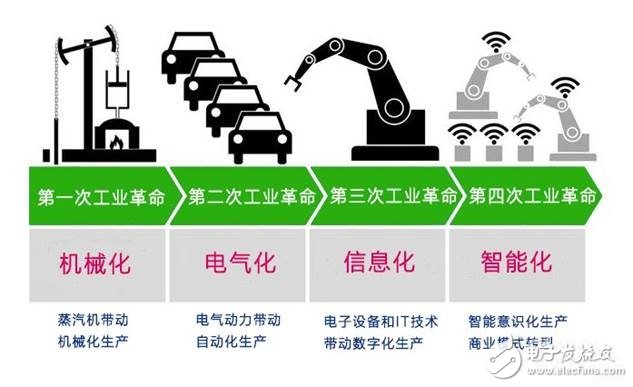
The first industrial revolution originated in the 18th century, creating an era of replacing manual labor with steam engine power, which triggered the war from the cold weapon era into the era of hot weapons; the second industrial revolution occurred between 1870 and 1914, creating electricity Instead of the steam power era, the war entered the era of mechanization; the third industrial revolution began after World War II. The informationization and digital revolution made the traditional industry more mechanized and automated, and the war entered the information age.
The fourth industrial revolution is coming, this is an intelligent era. The background of the trade war is nothing more than a war in an intelligent era.
Since the outbreak of the global financial crisis in 2008, the economies of the traditional powers in Europe and the United States have been hit hard, prompting them to re-recognize the importance of manufacturing, and have proposed a “re-industrialization†revitalization plan, which aims to restructure the manufacturing chain by upgrading high-end manufacturing technology. Drive economic development and employment. 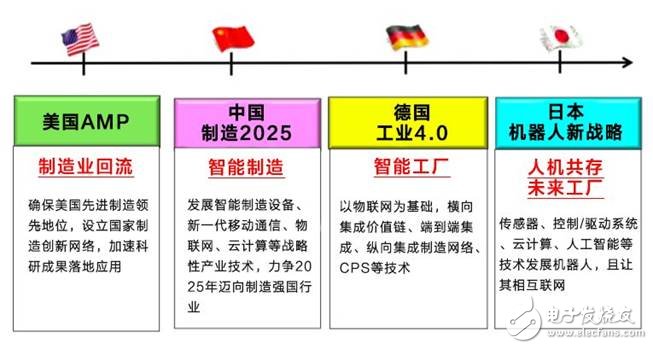
The United States launched a trade war is not a whim. As early as June 2011, the Obama administration launched the US Advanced Manufacturing Program (AMP), proposing a “manufacturing return†to ensure US advanced manufacturing leadership and establish a national manufacturing innovation network (NNMI). ), to accelerate the application of scientific research results.
In 2011, Germany proposed "Industry 4.0", and its core system CPS (Cyber-Physical System) portrayed a hacker-like scene in which the virtual digital world and the physical world intersect.
In the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†proposed by China in 2012, smart manufacturing, next-generation mobile communications, triple play, Internet of Things, and cloud computing are listed as strategic industries. In 2015, China announced the implementation of “Made in China 2025†and strived to become a manufacturing country in 2025.
In the meantime, Japan also proposed the "Japan Industrial Revitalization Plan" and the new robot strategy to revitalize the manufacturing industry and respond to the aging of the population; South Korea proposed "Manufacturing Innovation 3.0" to encourage manufacturing transformation and development, and promote the IT industry, The integration and development of major industries and new industries.
China's "Made in China 2025", the "AMP" in the United States, and the "Industry 4.0" in Germany are collectively referred to as the fourth industrial revolution. They all aim to use the major breakthroughs in science and technology to promote major changes in the economic and industrial structure. So, what is the fourth industrial revolution?
What is the fourth industrial revolution?
The fourth industrial revolution is collectively referred to as Industry 4.0, and its core content can be simply summarized as: one, one network, three integration.
One: Manufacturing Service Manufacturing “Manufacturing Service†is the future trend. By 2025, manufacturers will get more revenue from services, not just products.
The so-called manufacturing service industry means that manufacturers will undergo fundamental and subversive changes in the entire product life cycle, such as logistics, product design, workshop automation and customer relationship management, to achieve value chain expansion and shift from a single sales product. Provide products and services.
Three integration: horizontal integration, vertical integration, end-to-end integration, horizontal integration, so-called horizontal integration, refers to the seamless integration of enterprises or horizontal integration of value chain from procurement, production to sales to ensure the entire value chain Every step of the game can be controlled in real time, providing real-time products and services.
This process will have a huge impact on traditional product design, manufacturing, sales and maintenance methods. The industry will reshuffle, new players will emerge, and traditional players will disappear, which will also enable traditional manufacturers to transform into integrated product service providers.
This horizontal integration also means that today's "Taobao model" will eventually be eliminated.
Vertical integration An enterprise usually has multiple information systems that are vertically aligned with each other like a chimney. Vertical integration is to connect these “chimneys†to achieve seamless connection of all links within the enterprise to improve production efficiency and achieve customized production.
End-to-end integrated end-to-end integration refers to the integration of the product's entire life cycle. It establishes long-term relationships with customers and products sold through the network, and continuously optimizes or redesigns products from customer or product feedback data to achieve “productsâ€. From the center to the "product service-centric" transformation.
To achieve "three integrations", the ICT infrastructure is the foundation and the key requires a network.
The core system of Industry 4.0 proposed by Germany is called CPS (Cyber-Physical System), which is defined as a system in which a virtual digital world and a physical world meet. CPS integrates ICT and control technology into traditional industries. In the use of Internet of Things, cloud computing, big data, artificial intelligence and other technologies to achieve automatic analysis, judgment, decision-making and learning growth to assist or replace human decision-making. 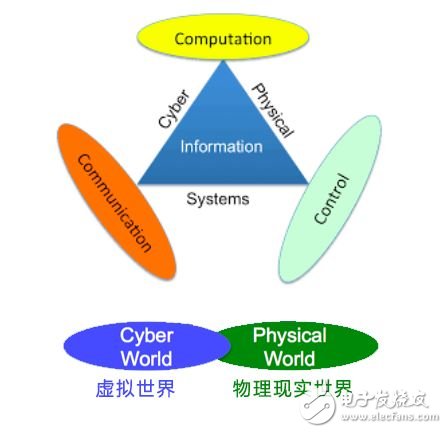
Obviously, CPS needs to support the 5G network of big data analysis, artificial intelligence, cloud computing and other technologies. 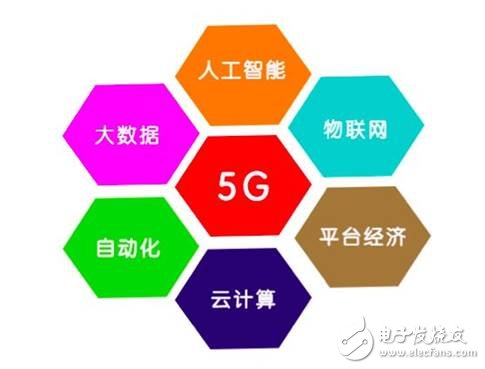
What does 5G mean for Industry 4.0?
The high-performance wireless network connects the massive sensors, robots and information systems in the factory, and the massive data and high-quality data generated by the connection continuously “feed†artificial intelligence, and feedback analysis and decision-making to the factory. At the same time, the 5G wide coverage of the Internet of Things Cover the globe, connect widely distributed or cross-regional goods, customers and suppliers, and maintain a full connection to the entire product life cycle, enabling vertical, horizontal integration and end-to-end integration within and outside the plant. 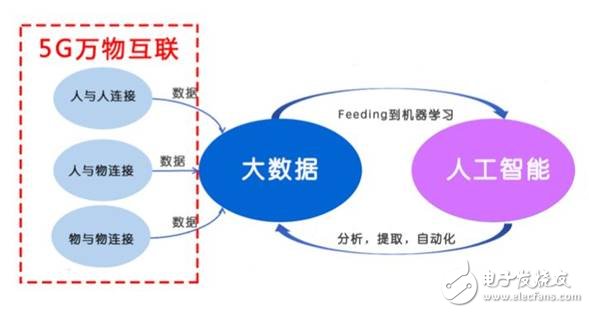
In short, the future factory is a combination of digital virtual and physical reality. ICT technology is integrated with modern manufacturing to improve the flexibility, traceability, versatility and production efficiency of industrial production, opening up new business models for the manufacturing industry. . The boundaries between the interior and exterior of the factory are becoming increasingly blurred. The factory is no longer an independent closed entity, but a part of a large value chain and ecosystem. This is called a “virtual factoryâ€. 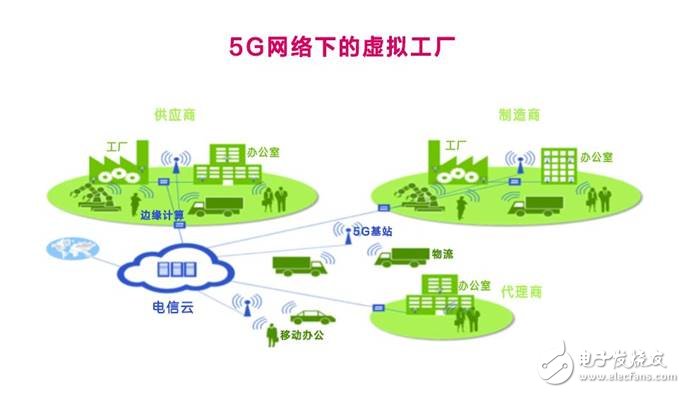
How 5G drives Industry 4.0
Drive Industry 4.0, relying on three key 5G technologies: New Air Port (NR), network slicing and edge computing. 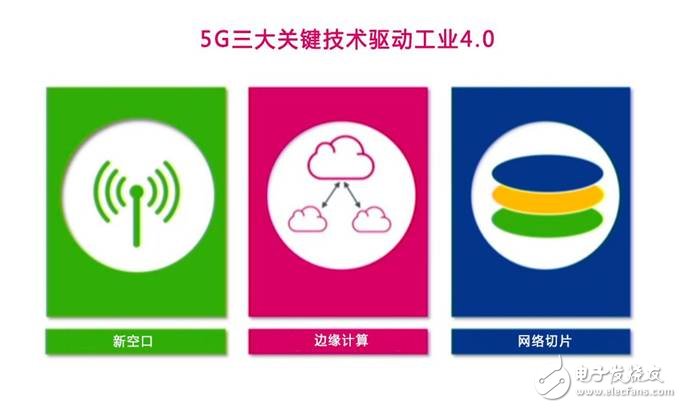
The new air interface here refers to the 5G wireless connection capability. As we all know, 5G defines three scenarios of eMMB, URLLC and mMTC, eMMB refers to high-speed connection, URLLC refers to ultra-low latency and ultra-reliable connection, mMTC refers to ultra-large-scale connection, Industry 4.0 These three scenarios will be applied to. 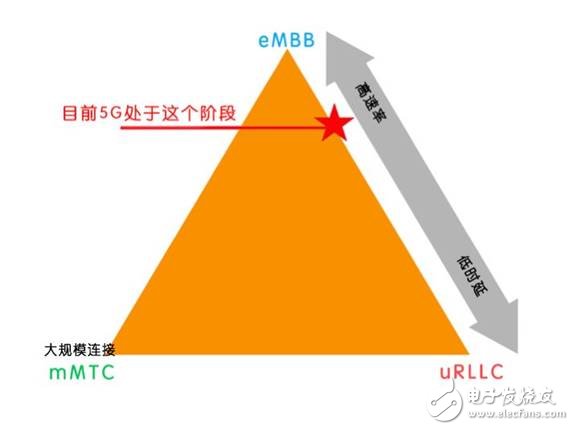
Take the four typical connections of the future factory: mobile robots, factory automation, new human-machine interface and logistics as an example to see how they correspond to the three major scenarios of 5G. 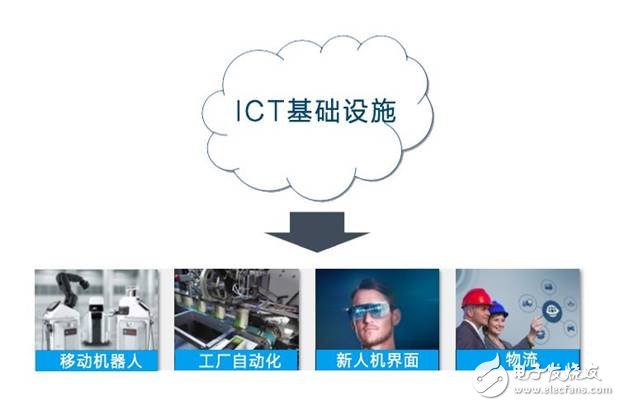
Mobile robots Mobile robots belong to the category of “flexible factoriesâ€. The so-called flexible factories refer to freely movable machine equipment and free reloading production tools to ensure that factories can quickly and cost-effectively switch production between different types of product lines. , adapt quickly to change.
To implement a flexible factory, a wireless connection is required to replace the existing wired connection in the factory. Only by getting rid of the constraints of the cable can the freely design, operate and upgrade the connected machines and robots.
However, it is well known that wireless connections are generally less stable than wired connections, so this requires an ultra-reliable ultra-low latency wireless connection, a 5G URLLC scenario.
Factory automation is in the automation factory. In order to improve the efficiency of the production line, real-time monitoring of each sub-component is required, real-time measurement of the quality of the produced product, and real-time optimization of the production line, which requires ultra-low latency and high reliability. Wireless connectivity, at the same time, applications such as visual control robotic arm, 3D model transmission, and remote digital factory require highly reliable high-bandwidth communication. Therefore, it is necessary to support mMTC, eMMB, and URLLC.
New Human Machine Interface (HMI)
Early human-machine interface refers to some serial communication in industrial control equipment. For example, inverter, DC governor, temperature control instrument, digital acquisition module, etc. can be connected to HMI to realize human-computer interaction function.
The future human-machine interface application will undergo a subversive change. With the integration of industrial intelligence and big data, wearable industrial equipment and augmented reality (AR) play an important role in human-machine integration, such as letting workers wear robots. Exoskeleton equipment, using "wearable industrial equipment + AR technology", integrate information with real-world scenes, capture information at any time, receive cloud commands and operational assistance, etc. This requires the network to support eMMB and URLLC two scenarios. 
Logistics In terms of logistics, from intelligent warehouse management to logistics and distribution, it requires wide coverage, deep coverage, low power consumption, large connections, and low-cost 5G IoT connections, which corresponds to the 5G mMTC scenario.
In addition, the end-to-end integration of the virtual factory spans the entire lifecycle of the product, connecting a wide range of sold merchandise, as well as low-power, low-cost and wide coverage of the 5G IoT, which also corresponds to the 5G mMTC Scenes.
Horizontal integration within the enterprise/enterprise also requires ubiquitous, seamless 5G networking. “Designing anytime, anywhere, anytime, anywhere†is the ambition of a smart factory, which requires the network to adapt to the changing capacity and mobility requirements, and to flexibly integrate different wireless access technologies. Therefore, the inclusiveness of 5G networks And the diversity of support business is indispensable.
In summary, the future factory is inseparable from the 5G connectivity, but the 5G network requires a network to support eMMB, URLLC and mMTC. It is inseparable from another key technology - network slicing.
Network slicing We should explain network slicing more than once. The so-called network slicing is to cut a physical network into multiple independent and logical slice sub-networks. These "slice networks" share physical infrastructure and provide different service types to deal with different scenarios. 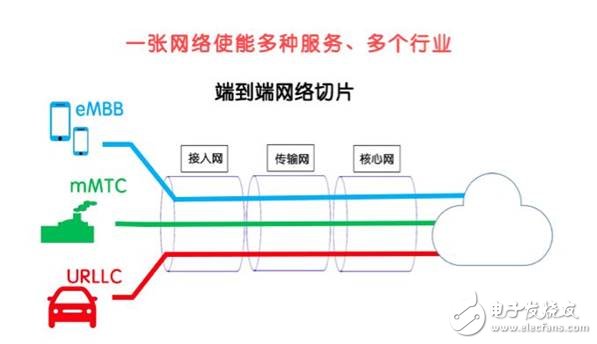
We often compare the 4G network to a high-speed transportation system. You can compare the 5G network slice to a comprehensive urban transportation system. There are roads, subways, light rails, BRTs, sidewalks, bicycle lanes, etc. Different transportation systems respond to different people. Demand.
To create and manage network slices, you need two major technologies, NFV and SDN.
NFV, the virtualization of network functions, is divided into three layers in the horizontal direction: physical resource layer, virtualization layer and service layer, and vertical is the NFV management orchestration (MANO) layer. 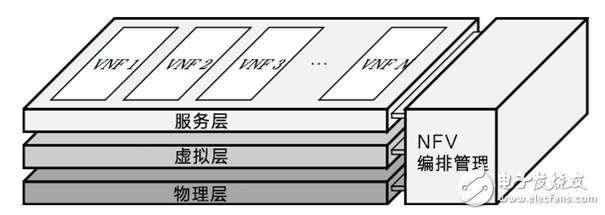
â–²NFV architecture
â— The physical resource layer refers to the underlying physical resources such as computing, storage, and network.
â— Virtualization layer refers to a set of virtual resources used to deploy and execute network functions. It virtualizes the underlying physical resources and shares the underlying physical resources in the form of virtual machines (VMs). A virtual machine can contain a certain number of calculations. And storage resources.
The service layer is composed of a series of VNFs (virtual network functional units) constructed by virtual resources. The VNF can be understood as a modular software functional entity corresponding to existing physical network elements in the network.
â— The above three layers are managed by MANO. MANO allocates resources according to requirements and configures physical and virtual resources for NF (network function).
NFV is responsible for the virtualization of various network elements, which decouples the traditional telecom equipment hardware and software. SDN is mainly responsible for separating the control plane and data plane of each network node, and extracting the control plane to form an independent and centralized Controller (SDN Controller), this controller is equivalent to the central brain of the network. It looks down the entire network from a higher level, and issues instructions to uniformly manage multi-layer forwarding in the network. Control signaling is no longer word-of-mouth. Instead, focus on intelligent management. For example, if the network is likened to the human body, the human body's eyes, ears, nose, hands, feet and other human organs correspond to different NF (network function), then SDN is equivalent to the brain, controlling the coordination of various organs. 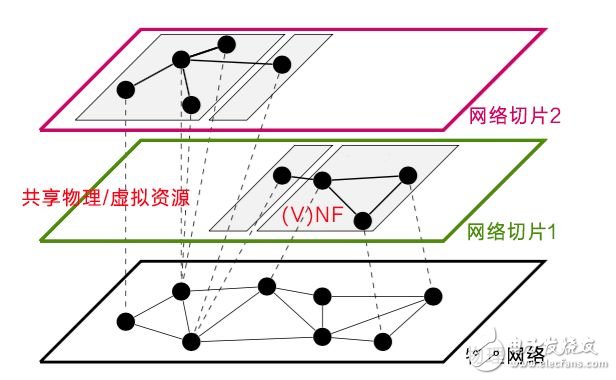
Based on NFV/SDN technology, a 5G physical network is "cut" into multiple logical networks to serve different scenarios of Industry 4.0.
Network slicing also has a key feature - end-to-end QoS guarantees. Traditional wireless services are offered in a "best effort" manner, with everyone sharing network and wireless resources, but industrial applications require more stringent QoS (network quality of service), and network slicing not only provides end-to-end QoS guarantees, but also Can isolate different services to meet the different service needs of future factories.
After the operator created a personalized network slice for Industry 4.0, each network slice satisfies different use cases and industry-specific requirements, which opens up a new, customized network slice-as-a-service (NSaaS) service model. In the future, traditional manufacturers will transform into integrated product service providers, laying the foundation for introducing new business models and business ecosystems. We will see more network slices and network sub-slices applied to Industry 4.0 in the future. 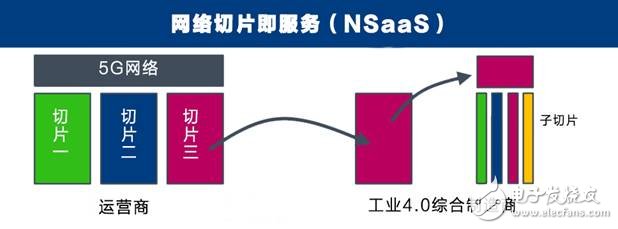
The above introduction to network slicing is a bit abstract, let's take an application case. 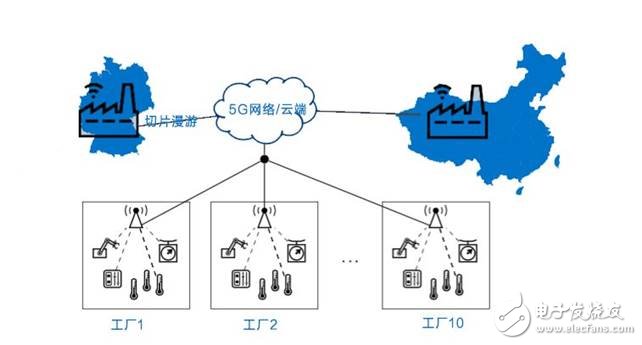
Take custom pharmaceuticals as an example. Suppose a pharmaceutical factory has 10 branches around the world. The pharmaceutical process in each branch is the same, that is, by controlling the pipette mounted on the robot arm to distribute the drug components of the drug. Different from the previous pharmaceutical process, it is now called “customized pharmaceuticalsâ€, which means that the types and quantities of pharmaceutical ingredients are distributed according to different types of patients. To this end, the 10 branches are connected to the cloud through 5G networks, and the cloud storage is massive. Patient information data, and through the big data analysis and artificial intelligence to determine the drug composition for different types of patients, in the production process, the robot arm needs to connect to the cloud through the 5G network in real time, and according to the instructions of the cloud, the drug is dispensed in real time.
This case corresponds to the 5G URLLC scenario and can be implemented by relying on 5G network slicing with end-to-end QoS guarantee. At the same time, in the production process, workers use the new human-machine interface (HMI) such as wearable devices and AR technology to monitor the production process, enhance the display of video from the cloud in real time, and install numerous sensors on the production line to realize automated processes. These scenarios also require other 5G network slices to implement.
In order to guarantee end-to-end QoS, another key technology is very important in dealing with ultra-low latency and ultra-reliable scenarios in Industry 4.0 - edge computing.
Edge Computing Edge computing refers to sinking the computing and storage capabilities of the cloud to the edge of the network, bringing it closer to the client, not only reducing network latency and load, but also deploying new applications locally. 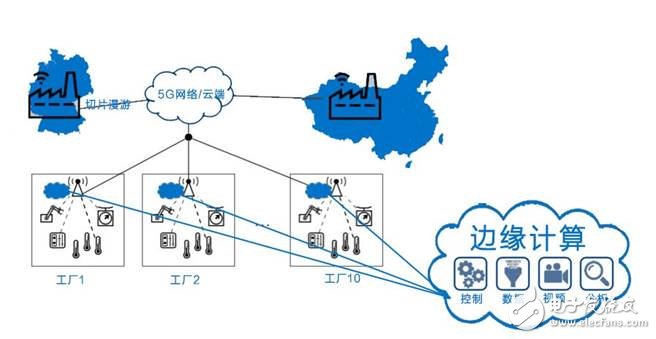
Edge calculation is the cornerstone of Industry 4.0 and a catalyst, mainly in the following aspects:
â— Low latency Edge computing is deployed locally, which means that it can provide ultra-low latency, which is very suitable for factory automation environment, so it goes without saying. Another big benefit of low latency is the ability to inspire innovative applications, such as the introduction of new human-machine interfaces to introduce off-site synergistic augmented reality.
â— Security Industry 4.0 connects the machines, assets, etc. in the factory through the network and connects to the external cloud through the network, which increases the flexibility and automation level of the factory, but it also means that it is more likely to be attacked by the network. Edge computing stores and processes as much data as possible on the edge without having to send it to the cloud, reducing security risks.
â—Integration Edge computing not only does not require all data to be sent to the remote cloud, it also integrates locally with plant-floor data, ERP systems, and other cloudless systems for vertical plant integration.
â— Low-cost intelligent manufacturing collects and analyzes data from networked sensors, and makes real-time decision-making and predictive maintenance. These data volumes are increasing, which brings huge cost pressure to data transmission, calculation and storage. Edge computing Data can be collected intelligently, filtering useless data, thereby reducing costs.
In addition, some of the plant capabilities of future plants can be deployed to edge computing through virtual entities, further enhancing plant flexibility and scalability.